IMPORT EXPORT
Import and export are fundamental components of international trade, enabling the exchange of goods and services across borders. Importing refers to the purchase and transport of goods and services from foreign countries to the domestic market. Conversely, exporting involves selling and shipping domestic goods and services to foreign markets. These activities are crucial for economic growth, allowing countries to obtain products not available domestically, benefit from cost advantages, and access larger markets for their goods.
Import and export processes involve various regulatory measures, including tariffs, customs duties, and trade agreements, designed to protect domestic industries and facilitate fair trade. Efficient logistics, robust supply chain management, and adherence to international standards are essential for the smooth flow of trade. Additionally, businesses engaged in import and export must navigate currency fluctuations, cultural differences, and political factors that can impact trade relations.
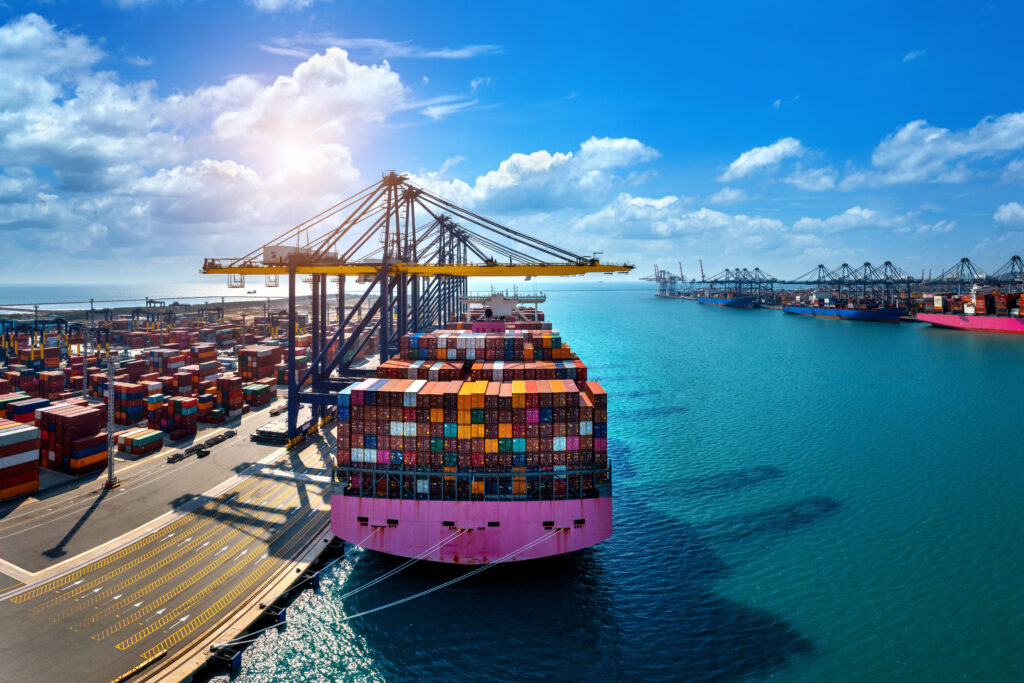




Import and export activities contribute to global interconnectedness, fostering economic partnerships and cultural exchange. They enable businesses to diversify their markets, reduce dependency on local economies, and enhance competitiveness. By leveraging global resources and market opportunities, countries can achieve economic diversification, improve living standards, and promote innovation and technological advancements.
